 amplify / Nope, it really is no longer an Xbox, Playstation, or perhaps a Dreamcast... Macgeek.org's Museum reader feedback forty five Share this story
amplify / Nope, it really is no longer an Xbox, Playstation, or perhaps a Dreamcast... Macgeek.org's Museum reader feedback forty five Share this story Apple in mid-1993 was reeling. Amidst declining Mac income, Microsoft had received a stranglehold over the pc industry. Worse, the outdated 12 months Apple had spent $600 million on analysis and construction, on products reminiscent of laser printers, powered audio system, color displays, and the Newton MessagePad equipment—the first equipment to be branded a "personal digital assistant," or PDA. however little return had yet come from it—or indeed looked prone to come from it.
The Newton's unreliable handwriting awareness became right away becoming the butt of jokes. including to the turmoil, engineering and marketing groups have been readying for a radical transition from the Motorola 68k (often known as the 680x0) household of microprocessors that had powered the Mac seeing that 1984 to the PowerPC, a brand new, more potent laptop architecture that was jointly developed via Apple, Motorola, and IBM. Macs with 68k processors wouldn't be capable of run application constructed for PowerPC. in a similar fashion, application developed for 68k Macs would should be up to date to take skills of the superior PowerPC.
It turned into during this ambiance that COO Michael Spindler—a German engineer and strategist who'd climbed through the ranks of Apple in Europe to the very suitable layer of govt administration—turned into accelerated to CEO. (The outdated CEO, John Sculley, become requested to resign.) Spindler spearheaded a radical and value-heavy reorganisation of the business, which harmed morale and accelerated the chaos, and he developed a acceptance for having horrendous people abilities. He'd hold conferences through which he'd ramble incoherently, scribble illegible notes on a whiteboard, then go away earlier than any one could ask a question, and his office changed into constantly closed.
About modern excerpt
This characteristic is excerpted, in a little bit modified form, from the new e-book the secret historical past of Mac Gaming with the aid of longtime Ars contributor Richard Moss. although the booklet's liberate is firstly abroad, US readers can still currently purchase the e-book through Amazon UK ahead of its US unencumber later in 2018. The publication is additionally attainable in e-codecs via retailers such as Unbound, iBooks, and Amazon.
beneath Spindler's rule Apple grew to be increasingly dysfunctional. The enterprise misplaced focal point and direction. twelve months the board decided to drop Mac expenses to raise market share, the next they backflipped and chased gains. Innovation all however disappeared from their product line, and now they embraced a concept lengthy abhorred internally: sanctioning Mac clones.
The Mac had reached 12 p.c share of the personal desktop market in 1993, best to automatically begin its decline as the laptop, which turned into outselling the Mac ten-to-one, ticked over ninety % right here yr. Apple's board and senior executives theorised that permitting different companies to fabricate Macintosh hardware would somehow reverse this style—that Apple may beat Microsoft on the licensing game and overturn their massive market share deficit.
Apple had licensed the Mac device before, however simplest for specialised makes use of in new markets—things that didn't compete with Apple's Mac earnings. Eric Sirkin, director of Macintosh OEM products within the New Media Division, had brokered deals for Mac OS for use in embedded systems—computer systems with dedicated, certain services. (OEM, or original machine manufacturer, is when a product is licensed to be resold as an element or subsystem in yet another enterprise's product.) however when the clone application started, he wasn't involved. He doubted the cost of other corporations selling buyer Macs, so he stayed clear. soon after, through indirect channels, Sirkin received wind of an approach with the aid of a big japanese toy business known as Bandai to make a Mac- primarily based games console. It changed into in the territory of the newly shaped very own Interactive Electronics (PIE) division, run with the aid of former Philips Electronics vice-president Gaston Bastiaens. "They weren't capable of capitalise on the opportunity," Sirkin remembers, which pissed off one of the individuals in the PIE neighborhood.
Sirkin turned into already managing a project (the FireWire communications interface) that worried common shuttle to Japan, so he was chuffed to appear into it. His PIE group colleagues linked him with Bandai, and off he went to Japan talk about their idea.
centered in 1950 by way of the son of a rice service provider, Bandai had grown into one of the largest toy producers in the world. It had made typical toy vehicles within the 1960s and Seventies, and with the aid of the Nineteen Nineties was the toy licensee for most of the familiar eastern little ones's manga and anime—together with Ultraman, tremendous robot, Gundam, Dragon Ball, and Digimon. The enterprise had been making waves in the American market as the maker of the motion figure toys for the hit new infants's superhero tv show Mighty Morphin vigour Rangers, which turned into according to a japanese display known as tremendous Sentai. In 1994, Bandai would generate $330 million in salary from earnings of power Rangers merchandise within the US alone.
CEO Makoto Yamashina, the son of the founder, wanted Bandai to be more than an motion-determine toy enterprise, however. He saw their future as a worldwide amusement enterprise like Disney or Nintendo. He had pushed for years for Bandai to supply its own animated movies and television serials and to delve deeper into domestic electronics. in the manner, he tremendously various their product line. They made sweets, bathing room products, garb, videos, dolls, robots, motion figures, and video video games. The older Yamashina as soon as publicly lamented his son's company approach of bringing out ten toys within the hope that three would become hits.
but Bandai had grown significantly in each stature and salary due to the fact that Yamashina had taken over in 1987. Now he had an idea that could enable the business to tackle the giants of home amusement. Bandai's thought centred around the CD-ROM, which changed into surging in recognition as CD drives dropped in price. Myst, a video online game, was frequently the primary element people purchased. and many of Bandai's licenses, including Dragon Ball Z, vigour Rangers, and Sailor Moon, have been ultimate for the games market. Bandai saw an opportunity to leverage these homes and the CD format together, and to thereby triumph over the lounge. They admired Apple and the Mac, in order that they hoped to accomplice with the Cupertino business in developing and releasing a online game console and multimedia computing device. more advantageous yet, if the equipment can be a reasonable, extra specialised Mac then they could avoid the problem dealing with the similar 3DO system —which had restrained application purchasable.
It become complicatedIt fell to Eric Sirkin to explain that Apple, in its present state, would doubtless now not be inclined, or able, to launch it as an Apple-branded product. "My charter become to create opportunities for the Macintosh outdoor of its core market," he says. A stripped-down Mac packaged as a living room multimedia equipment may healthy the charter, however only on the proviso that it was neither built nor sold by means of Apple. Sirkin defined that what Apple might do become lead the engineering and design of the product and then charge a per-equipment licence fee to Bandai. The manufacturing, marketing, and branding would all be Bandai's responsibility.
They preferred that idea. So we went via a sequence of conferences, going back and forth, and commenced involving Satjiv [Chahil], my boss, who also raised it to the consideration of Ian Diery [head of Apple's personal computer division], so we had all the visibility in what we have been doing. It was considered as an pastime not costing the enterprise some huge cash and maybe having a chance to reposition the know-how of the business in one other market.
Apple and Bandai quickly entered into an agreement. Sirkin returned to Cupertino and put a team of engineers onto the mission to aid him design the equipment internals. They codenamed the assignment Pippin, after the class of apple, because the name was already registered by means of Apple and it hadn't been used yet.
The core expertise would come from the Macintosh—in particular the brand new PowerPC line. To maintain prices down, they opted for the low-conclusion PowerPC 603 in place of the extra effective however lots extra high priced 604 processor. The Pippin, then, can be a affordable Macintosh designed for the lounge. A clone by way of a distinct name, for a distinct purpose.
instantly, things got complex. Sirkin and his team had been recommended through Apple management to make the gadget un-Mac-like. Pippin could not be allowed to cannibalise laptop Mac sales. It had to be so limited that people couldn't perhaps use it as a main personal desktop.
This distancing from the Mac affected the Pippin in a number of techniques. First, Apple deemed it vital that the device be each manufactured and branded as a Bandai product. "The Bandai individuals would have cherished to have Apple just go off and make it," recalls Richard Sprague, who acted as middleman and interpreter between Apple and Bandai. "however they felt like manufacturing was the cost that they needed to pay to get an Apple-suitable media gadget."
Apple's company americans believed that the precise funds within the desktop business came from software. "The problem with utility is that people copy it," they'd argue, "so we're going to position the top-rated replica coverage on it that humankind has ever conventional. we're going to make this aspect so locked down that it is going to be not possible for them to play anything else other than the stuff we put out." This, Sprague says, ended in some sick-advised mathematics that spurred ill-suggested guidelines:
it will had been nice to have a $200 desktop the place you're taking a duplicate of Myst off the shelf that works on a laptop, it works on a Mac, and simply pop it into the Pippin and have it play. that might be sort of cool. but no, we had to make it so that the Myst builders would make a distinct edition of their disc just for us. It was an entire bunch of issues identical to that that were about guaranteeing that no one would ever mistake it for a Macintosh.
Sprague had been employed by using Apple in 1991 to assist recruit jap utility groups to write down application for the Mac. "In these days Apple became in fact becoming right now in Japan," he recollects. "From each viewpoint it looked like the japanese have been going to dominate the world in all types of things. So it became sort of a hot, special location to be." Sprague become also a fluent eastern speaker, so he regularly had to play the function of interpreter for travelling Apple executives. at some point he bought dragged alongside to a "tremendous correct-secret meeting" between New Media Division head Satjiv Chahil and Bandai's right executives, together with business president Makoto Yamashina.
"somewhere in the core of the meeting it turned out that Bandai became really mad at Apple," Sprague remembers. "[Yamashina] changed into like in his most well mannered but form of imply eastern talking about how Apple had screwed him over—how they'd signed this settlement months ago and now Apple hasn't achieved a single aspect." Apple become presupposed to have put a full-time employee in Japan to work with Bandai.
Satjiv, with out batting an eye, he says, "smartly we did hire a full-time grownup. this is why I introduced Richard Sprague." He advised me to translate that. i am like "Satjiv, I've already got a job. or not it's not this. i was just dragged alongside because you requested me." He goes, "just play alongside. just inform him this. i'll make it up later." lots of Pippin turned into run exactly that way. just kinda making issues up as we go.
Apple's increasing managerial dysfunction took a extra instant toll on the Pippin mission. "We went via all types of struggles in the engineering crew," Sirkin remembers. At one point 4 key software engineers went on strike. "They noted they couldn't carry the product on the schedule committed and that they'd decided they failed to are looking to work on it anymore after engaged on it for like six months," Sirkin continues. "i stopped up having to fire them." of their area he assigned a gaggle of alternative utility engineers from his community who were willing to work time beyond regulation to get the undertaking lower back on agenda.
checklist graphic with the aid of Wikimedia, taken by Evan Amos
Third birthday celebration pitfallsPresto Studios programmer Bob Bell remembers how stark this change turned into for third-birthday party relations. He became working on the Mac and Pippin models of The Journeyman assignment: Pegasus prime, a remake of the primary Journeyman mission adventure game. "It felt just like the historic shield had been changed with the aid of these younger whippersnappers," he says. the place the old crew didn't appear to care lots, this new group were "go-getters" who confirmed a real pastime within the project and answered at once to queries.
extra studying The state of Mac gaming That became high-quality news for Bell, who had his arms full deciding how to get Pegasus leading to run fluidly off a CD-ROM (on Mac, the Journeyman undertaking games put in most of the content material to a person's tough power). Presto had pioneered an animation know-how that would play micro-motion pictures to transition from one mounted vicinity to another. This worried opening and shutting info time and again once again, which changed into plenty, an awful lot slower on a CD. "So I decided i'm simply gonna make one colossal film," Bell explains. Pegasus leading on the Pippin would open the movie containing all the going for walks animations for a stage at launch, examine in a knowledge constitution that specific what frames corresponded to what locations, then push the central frames to the foreground as they were necessary. "i would not ever shut the movie," Bell continues, "and that made it a great deal quicker."Bell was excited by using the Pippin. He thought it gave the impression to be on the cutting edge—a groovy machine that might definitely get massive. "I certainly not notion of it as underpowered, or just like the acceptance it has today of 'the worst console in heritage' or whatever thing," he says. as an alternative, he idea it changed into enjoyable and challenging. sure, it had low reminiscence and no hard drive, however then so did the different game consoles of the time. And he appreciated that, unlike his colleague engaged on the psversion of Pegasus best, he could leverage Apple's QuickTime library.
Bell wasn't the only 1 who thought Pippin had promise. "on every occasion we referred to the words 'Dragon Ball' and 'energy Rangers' and whatnot," Sprague recalls, "individuals got truly excited because they concept, 'Wow, this is going to be a real powerhouse.'" The americans inside Bandai have been completely at the back of the assignment, too. Sprague remembers that they'd studied the video games industry inside-out and believed that Pippin became their future.
That made things frustrating. "Yamashina, the appropriate guy—this was his no 1 priority," he recalls. "anything else we necessary from Bandai become a mobile call away. There was no difficulty with money or supplies. the entire top of the line people were working on it. Whereas with the Apple facet it became the accurate opposite."
"Yamashina would come to Cupertino because there can be some difficulty happening that must be addressed and nobody would meet with him," Sprague continues. desirable-ranking executives had little time for the mission. "They concept it was a dumb thought," he says.
Sirkin remembers how Pippin's pre-launch buzz briefly earned the attention of Apple's senior administration—for better or worse:
Pippin was so a success ahead of launch that the executives decided it was such a constructive undertaking and Eric—being me—did such an excellent job we had been break up in half. They put the advertising community in this division and the engineering group in another division, and that become going to aid the project—which of course became absolutely idiotic and had the contrary effect because one of the most factors we had been successful become that we had all of the resources in a single business enterprise.
The decline: "You cannot make cash on the cyber web"The Pippin team struggled on, pulled this fashion and that by means of territorial executives. "I remember being in a heated argument with people inner the Pippin group," Sprague recalls, "the place it become the smartest americans within the room—they're all these MBAs and that they're like 'that Netscape aspect is kinda cool.' but it surely's no longer extremely good, they argued. There are a lot of things it can not do. And furthermore, this cyber web aspect is rarely going to turn up 'since you can not make cash on the web.'" They insisted that the way to make cash online was with walled-garden on-line functions like AOL and Apple's personal eWorld—which had email, information, chat, and group features that required a subscription price to access. Sprague continues:
Bandai [then] came to us and mentioned, "have you ever guys viewed this cyber web aspect? This Pippin will be the best approach for people to get onto the cyber web. You may make a collection-suitable field ... so that now americans can adventure the internet from their couch within the front room, and individuals who don't know a way to use a keyboard—who aren't natural customers for a pc—all and sundry's going to head loopy after they see this factor." So we told them, "No, you can't put the information superhighway on this thing since it's a media player and the cyber web's not gonna make it. So just trust us. You do not wish to waste time and energy on anything that connects to the cyber web."
Bandai, to their credit score, didn't consider Apple. many of the americans they had on Pippin have been young and hip, at the cutting edge of eastern society, so that they regarded the expertise of the cyber web. They insisted that Pippin be allotted with a modem and the imperative application to get online. "That became their marquee title," Sprague says. "truly getting on the information superhighway."
meanwhile, greater outsiders had began to word the complications inherent in Pippin's design. One response in specific stood out to Sirkin. "We had a developer convention in California, which we hosted and Bandai co-subsidized," he says. Bandai flew a lot of japanese builders over whereas Apple subsidised the trip expenses of a number of American studios.
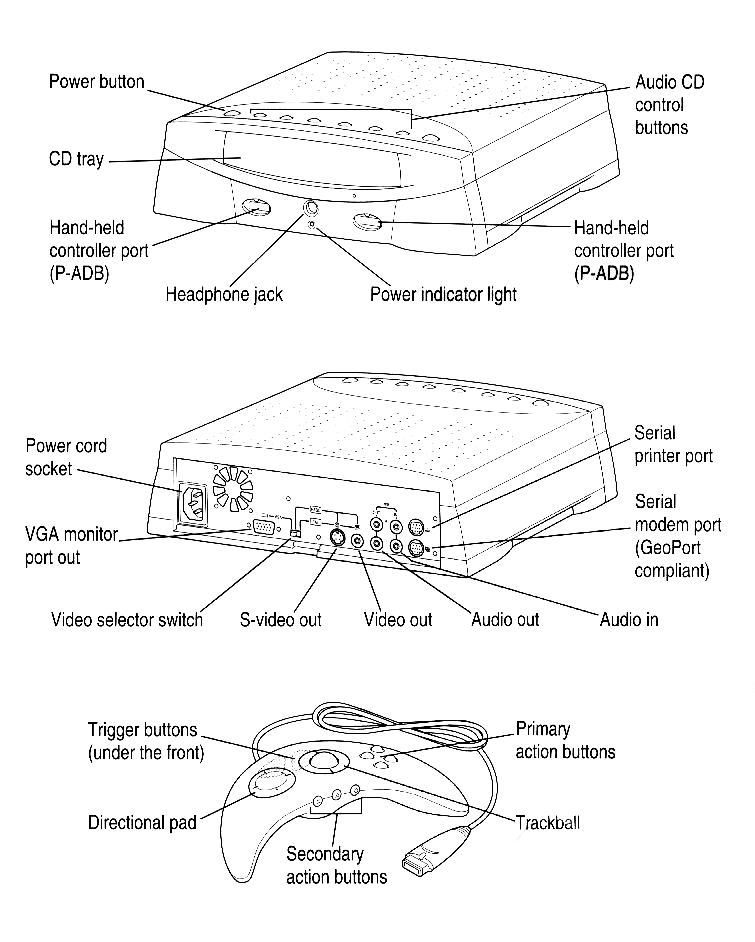
in the Q&A session at the conclusion of Sirkin's introductory speech, one developer stood up and requested, "neatly, what is that this game console going to do more desirable than the rest? Is it going to be an online machine? Is it gonna be a communications equipment? Is it going to be a superb game console?" Sirkin could not reply. Pippin wasn't wonderful at the rest. It could not do games in addition to a psor Sega Saturn, even though it become technically greater powerful than them, nor may it do everyday computing initiatives in addition to a computer Mac or computing device. It turned into a low-conclusion Macintosh with the difficult drive pulled out, a new pics engine brought in (so that it may look decent on a tv screen), and a heavily stripped-down working device (in order that it may well be loaded from a CD-ROM on startup) that might most effective run one application at a time.
There had already been an undercurrent of internal doubt about Pippin's short- term commercial skills, but this magnified Sirkin's own uncertainties. "It changed into like in no man's land," he says. "It became more costly than a video game console and it wasn't as effective as a laptop, so how do you explain it to the market? How do you position it?"
existing Mac game and multimedia developers have been courted to supply Pippin types of their work. Marathon creators Bungie, the Mac's premier online game developers, had been among those that signed on with hopes of achieving a brand new viewers and strengthening relationships with Apple and Bandai.
super Marathon, a Pippin port of Marathon and Marathon 2: Durandal bundled into one kit, become a nightmare task for sole programmer Jason Regier. The online game's keyboard and mouse controls needed to be shoehorned into engaged on the Pippin's bizarre boomerang-shaped AppleJack controller, which had four action buttons on its front, two trigger buttons on the true, three smaller buttons on the backside, a directional pad, and a trackball at its centre. He needed to redo text rendering in its many in-game computer terminals, since it needed to be readable from a stronger distance. memory constraints supposed song and different features needed to be reduce. And any technical issues he had needed to go through his colleague Alex Rosenberg's pals at Apple—as a result of Bandai US had taken over technical help and they weren't answering his queries.
The online game expertise community in Apple's Mac division later modified the GameSprockets technology—new construction libraries to assist Mac games operate more suitable—for Pippin to alleviate some of those concerns. nonetheless, as Pippin neared unencumber, they have been known as on for information through their pals at a number of important Mac game groups who wanted to post Pippin types of their big titles. "None of them deemed it profitable to finish the work," recollects Chris De Salvo, some of the engineers within the community, as a result of performance became so terrible.
simplest three Mac video games ever achieved the transition from Mac to Pippin: Bungie's Marathon/Marathon 2, 3D racing game Racing Days (which had probably the most most advantageous graphics yet viewed in its style), and Presto's Journeyman challenge: Pegasus leading. The rest of the Pippin catalogue consisted of a number of dozen multimedia and edutainment titles, reminiscent of Dragon Ball Z, Anime designer and Compton's Interactive Encyclopedia, and Japan-only games like Tunin'Glue and L-Zone.
Bandai expected its two Pippin models to promote 500,000 instruments international in a yr. They prepared to spend $one hundred million on advertising it closely in Japan and the us as a hip new thing with big cool ingredient. however the gadget's identity crisis would damage client reception. For a few hundred bucks more, they might purchase a a whole lot greater potent cyber web-competent desktop; for just a few hundred less, they could get a dedicated video games console with a large library of incredible video games like the PlayStation.
Apple's Senior Director of latest Media Operations, Steve Franzese, instructed the l. a. each day information that he expected Pippin to sell three million contraptions—throughout numerous manufacturing companions, no longer simply Bandai—in three years (at a royalty of lower than $15 per sale), with each software sale bringing in a $three royalty to Apple.
Pippin accomplished neither of these projections. Estimates latitude from simply 5,000 to 42,000 @WORLD devices offered in North the usa. revenue in Japan fared most effective a bit more advantageous, while in Europe, as the short-lived Katz Media KMP 2000, it bought significantly worse. (American electronics business DayStar Digital would later purchase Bandai's leftover inventory in 1998, whereupon they reportedly sold as many as 2,000 methods.)
where are they now? Eric Sirkin now runs a company he centered in 2014 called DiamondDox, which gives a cloud-primarily based service to look after people's electronic legacy. Richard Sprague spent sixteen years at Microsoft after the Pippin project; he's now the first Citizen-Scientist-in-residence at microbial genomics business uBiome. Makoto Yamashina stepped down from Bandai in 1997 after the business's center managers revolted in opposition t a planned merger with Sega. He now runs an funding fund.The Pippin venture turned into shut down in March 1997, when Apple laid off four,one hundred employees in a bid to stop the bleeding from its nevertheless-failing Mac business. Sirkin offered it for the chop, on the grounds that he knew it become as good as useless, even if his team had been diligently working to repair Pippin's issues with a 2d-generation model. "We had a real pics engine which may compete with the games consoles, and we had a stronger pix engine than we had within the first t echnology," Sirkin says. "And we did this on our personal, hoping that we would market this 2nd edition."
a part of the Pippin crew left before the mission was officially cancelled to birth their own enterprise and build a set-proper box with cyber web capabilities. They at last acquired purchased through sun Microsystems. Sirkin had no pastime in waiting around for Steve Jobs to come back lower back (which at that element wasn't a sure issue, regardless of Apple having simply bought Jobs" company, next), so he went off to birth an organization around the FireWire technology. The rest of the Pippin crew additionally left Apple.
In hindsight, Sirkin believes that Pippin become always destined for failure. It could not ever have survived within the Apple of its day:
It became schizophrenic. It was now not bound what it become going to be. And there was no patience in the enterprise. No interest in investing in whatever thing and iterating on it until you bought a market adopted for it. I definitely believed that if we had been given the probability to finished the 2d technology and circulation onto the third then it would have been a extremely a hit product. but that wasn't on the playing cards. It wasn't going to ensue.
Richard Moss is a author and technology/games historian primarily based in Melbourne, Australia. apart from his new book, the key background of Mac Gaming, he produces Ludiphilia, a storytelling podcast about how and why we play. you could follow him on Twitter @MossRC and browse his past work on every little thing from FireWire to gaming genres to GTA V Easter eggs on Ars.
Comments
Post a Comment